Prion disease treatment is on the verge of breakthrough with recent research showing promising therapeutic advancements for these rare, fatal conditions caused by misfolded proteins. Conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia represent a significant challenge in neurology, but the development of a gene-editing therapy offers hope to patients and families affected by these disorders. Scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have made strides in reducing the toxic prion protein in animal models, effectively extending their lifespans. This collaborative effort between scientists and patients underscores the importance of patient-scientist collaboration in the quest for effective prion disease treatment. As research continues to progress, the potential for a viable treatment is beginning to feel like a real possibility.
The quest for treatment options for prion diseases has garnered significant attention recently, particularly with advancements in genetic therapies. These devastating neurological disorders, including conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and hereditary forms such as fatal familial insomnia, have long posed significant challenges due to their aggressive nature. Innovative approaches focusing on gene-editing techniques are now being explored, paving the way for hope where there was once despair. The collaboration of researchers who have personal stakes in these conditions emphasizes the critical intersection between medical science and patient experiences. As these groundbreaking studies unfold, the horizon for tackling prion diseases appears brighter than ever.
Understanding Prion Diseases and Their Impact
Prion diseases are a group of rare but devastating neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the brain. These proteins lead to severe brain damage and a rapid decline in cognitive and motor functions. Notable examples include Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia, and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. Each of these conditions manifests uniquely, but they all share a common origin: the misfolding of prion proteins. This misfolding disrupts normal cellular functions, resulting in neurodegeneration and, unfortunately, death. The incidence of prion diseases remains low, but their impact on families and caregivers can be profound and devastating, often leaving loved ones grappling with the loss of memory, mobility, and identity of those affected.
The implications of prion diseases extend beyond the individual to entire families and communities. Characterized by a rapid progression and lack of effective treatments, these conditions require dedicated care and support systems. Family members often play a crucial role in caregiving, which can take an emotional and physical toll. As researchers delve deeper into understanding prion diseases, the focus also shifts towards patient-centric research. By ensuring that patients and their families are involved in the research process, scientists aim to create more effective therapeutic strategies that truly address the needs and concerns of those impacted.
Innovative Approaches to Prion Disease Treatment
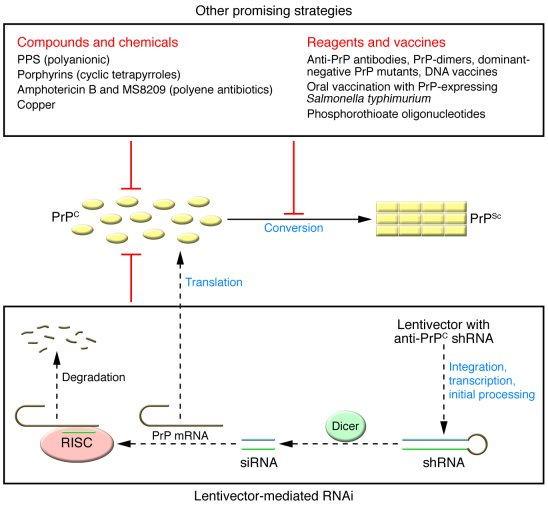
Recent advancements in gene-editing therapy represent a beacon of hope for treating prion diseases. Research led by experts at the Broad Institute has shown that a simple alteration in the gene responsible for producing malfunctioning prion proteins can drastically reduce their levels in the brain. Specifically, utilizing single base editing techniques, studies in lab mice demonstrated a remarkable 52% increase in lifespan following gene modification. These groundbreaking results mark a potential turning point, suggesting that similar strategies could be applied to humans suffering from conditions like fatal familial insomnia and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. The pathway to implementing these treatments in clinical settings, however, remains complex and will require comprehensive trials and safety evaluations.
The significance of patient-scientist collaboration cannot be overstated in this research landscape. Many of the researchers involved are not just scientists; they are patients themselves or have family members affected by prion diseases. This personal connection fuels an urgent drive to find solutions and accelerates the pace of research. For instance, Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, who have faced the reality of inheriting fatal familial insomnia, exemplify how personal experience can lead to informed, compassionate scientific inquiry. This collaboration bridges the gap between lab-based research and real-world applications, ultimately aiming for a treatment that not only extends life but improves its quality.
The Role of Gene-Editing in Prion Disease Research
Gene-editing therapy is at the forefront of revolutionary techniques aimed at combating prion diseases. By manipulating the genetic code responsible for the production of harmful prion proteins, researchers can effectively reduce their synthesis within cells. This method, developed through innovative collaboration at the Broad Institute, is a testament to how advanced technologies can be leveraged to create viable treatment options. Specifically, the use of a specially engineered viral vector to deliver the gene-editing tools directly to targeted cells has shown promising results in preclinical studies, paving the way for potential human trials. The elegance of this approach lies not only in its efficacy but also in its ability to directly address the root cause of the disease.
However, as hopeful as gene-editing therapy appears, the road to clinical application is fraught with challenges. It necessitates rigorous testing to ensure safety and efficacy, particularly given the dangerous nature of prion proteins. Researchers are currently focused on refining these gene-editing tools, making them safer and more effective for human use. This includes enhancing targeting mechanisms to minimize off-target effects in other tissues. The intersection of innovative therapies and patient insights is paving the way for breakthroughs that could redefine the standard of care for prion diseases.
Collaborative Strategies in Prion Disease Research
Collaboration is a cornerstone of modern scientific inquiry, particularly in the field of prion disease research. The unique challenges posed by these conditions have prompted a consortium of experts from various disciplines to unite their efforts. By pooling resources, knowledge, and techniques, researchers can expedite the development of treatment strategies and share valuable insights that might not emerge within isolated research pathways. This multifaceted approach allows for the incorporation of diverse methodologies, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes. Collaborative efforts are especially poignant in the realm of patient-scientist partnerships, where the lived experiences of those affected by prion diseases inform and shape research priorities.
One exceptional example of this collaboration in action is the relationship between patients and researchers like Vallabh and Liu. Their shared commitment to tackling prion diseases fosters a sense of urgency and motivation in the research community. Vallabh and Minikel’s personal journey inspires not only their work but also those around them, creating an environment that emphasizes empathy alongside scientific rigor. Such partnerships are invaluable; they enhance creativity in problem-solving and foster a culture of innovation that is essential for tackling the complexities of developing effective treatments for prion diseases.
Challenges in Prion Disease Treatment Development
Despite the promising advancements in gene-editing and other treatment modalities, the path to effective prion disease therapies is riddled with challenges. The unique biology of prion proteins complicates the drug development process. For instance, these proteins are notoriously difficult to study due to their infectious nature and ability to cause severe neurodegeneration. Moreover, there is a pressing need for extensive preclinical studies to assess the safety and efficacy of any new treatment before it can be considered for human trials. Each step in this daunting process requires meticulous planning, regulatory approval, and deep scientific insight.
Additionally, the sporadic nature of many prion diseases presents a challenge in understanding their full scope. Researchers must navigate the complexities of varying presentations and genetics among patients, which can inform how therapies must be tailored. The real-world implications of this variability mean that some treatments may work for specific mutations, such as those seen in fatal familial insomnia, while having limited impact on others like sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of not only the underlying genetic factors but also the patient population’s heterogeneity when developing effective treatment protocols.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Prion Disease Research
As research into prion diseases continues to evolve, the future looks cautiously optimistic. With groundbreaking studies revealing possible avenues for treatment through gene-editing and protein reduction, hope is growing for those affected by these devastating disorders. The commitment of researchers like Vallabh and Minikel reflects an industry shift towards integrating patient experiences directly into the scientific narrative, which is transforming research culture. Continued investment in innovative therapies, particularly those that harness gene-editing technology, is crucial for translating findings from the lab to real-world applications.
Furthermore, as more inter-disciplinary collaborations materialize, there is potential for significant strides in our understanding of prion mechanisms, which may unlock even more therapeutic possibilities. The continuous engagement of patient populations in the research process not only enriches the scientific approach but reinforces the urgency with which this work must proceed. Ideally, the amalgamation of cutting-edge research, patient input, and collaborative efforts will culminate in effective treatment strategies that make a tangible difference in the lives of individuals battling prion diseases.
Therapeutic Advancements in Neurodegenerative Disorders
The exciting advancements in treating prion diseases are part of a broader landscape of innovation in neurodegenerative disorder therapies. Traditional approaches to treating neurodegenerative diseases often focus on symptomatic relief rather than on addressing underlying biological mechanisms. However, with the advent of new technologies, such as CRISPR and other gene-editing therapies, there is a shift towards targeting the root causes of these debilitating conditions. Research is prioritizing the development of therapies that not only prolong life but also enhance the quality of life for patients currently suffering from prion diseases and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Additionally, the dialogue around therapeutic advancements is expanding with a strong emphasis on the importance of mechanisms like collaboration between researchers and patients. This transition towards a more collaborative research framework is imperative as it introduces diverse perspectives and drives more inclusive and patient-centered research trajectories. As scientists work together with patient advocates and those affected by prion disease, the focus remains clear: to foster innovative therapies that can fundamentally change the treatment landscape for all neurodegenerative diseases.
The Critical Importance of Patient-Scientist Collaboration
The integration of patient experiences into scientific research cannot be underestimated. In the field of neurodegenerative diseases like prion disorders, patient-scientist collaborations are emerging as a powerful catalyst for change. By involving those who understand the day-to-day realities of living with these conditions, researchers can gain invaluable insights that inform the development of effective therapies. This dynamic partnership has the potential to reshape therapeutic approaches, ensuring that researchers move in directions that genuinely address the needs of patients and their families.
Moreover, patient-scientist collaboration fosters a sense of community and shared purpose, strengthening the resolve of researchers to find innovative solutions to seemingly insurmountable challenges. As exemplified by Vallabh and Minikel, the drive to transform personal tragedy into meaningful scientific inquiry is inspirational. It not only energizes the lab but also fills a deeply felt need for breakthroughs that can change the landscape of prion disease treatment. The encouragement for surrounding teams to maintain this patient-centric focus is essential for creating meaningful advancements in science.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current status of prion disease treatment research?
Recent advancements in prion disease treatment research have shown promise, particularly through gene-editing therapy. Scientists have achieved significant breakthroughs in reducing harmful prion proteins in animal models, paving the way for potential treatments for conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia.
How does gene-editing therapy work in the context of prion disease treatment?
Gene-editing therapy aims to modify genes responsible for producing misfolded prion proteins, which cause prion diseases. By altering the genetic code, researchers have managed to halve the production of these proteins in laboratory mice, indicating a path toward effective prion disease treatment.
Can gene-editing therapy help patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease?
Gene-editing therapy holds potential for treating Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by targeting the genes that produce detrimental prion proteins. Ongoing research indicates that such therapies could eventually lead to improved outcomes for affected individuals.
What role do patient-scientists play in prion disease treatment research?
Patient-scientists, such as those affected by fatal familial insomnia, are integral to prion disease treatment research. Their personal experiences provide unique insights and motivation, driving the pursuit of therapeutic advancements in this challenging field.
What are the key challenges in developing a prion disease treatment?
Developing a prion disease treatment presents several challenges, including the complexity of safely delivering gene-editing therapies and ensuring that they effectively target only the affected cells. Additionally, navigating regulatory hurdles and conducting human trials will require meticulous planning and collaboration.
How are collaborative efforts impacting prion disease treatment advancements?
Collaborative efforts among researchers, including patient-scientists and technologists, are crucial for advancing prion disease treatment. Such partnerships facilitate sharing expertise and resources, ultimately accelerating the development of effective therapeutic strategies based on gene-editing techniques.
What is the significance of the recent paper published in Nature Medicine regarding prion disease treatment?
The recent study published in Nature Medicine highlights a milestone in prion disease treatment research. It showcases the potential of gene-editing therapy to significantly reduce prion protein levels in mouse models, suggesting a feasible approach for future clinical applications in humans.
What are the implications of successful gene-editing therapy for fatal familial insomnia?
If successful, gene-editing therapy could revolutionize the treatment of fatal familial insomnia by targeting the genetic mutations responsible for the disease. This may extend patients’ lifespans and improve their quality of life, marking a meaningful advancement in prion disease therapies.
What safety measures are taken in prion disease treatment research?
Researchers implementing gene-editing therapies in prion disease treatment take rigorous safety measures, including refining vectors to minimize any adverse effects and ensuring the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, all while adhering to strict ethical guidelines.
When can we expect human trials for prion disease treatments to begin?
While promising research is underway, human trials for prion disease treatments using gene-editing therapy are still several years away. Researchers must first complete additional preclinical studies and refine methodologies to ensure safety and efficacy before moving to human testing.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Research led by Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel aims to develop a gene-editing therapy for prion diseases. |
| Alterations to a gene have shown promising results in reducing toxic protein levels in mice, extending their lifespan by 52%. |
| Prion diseases include conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, with some cases due to inherited mutations. |
| The research indicates a potential pathway for effective treatment in humans, culminating from nine years of effort. |
| The lab emphasizes collaboration among experts, combining technology development with patient experiences for motivation. |
| Despite promising results, human trials are still years away due to the nature of prion research and safety concerns. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment is advancing towards hopeful possibilities, as recent research indicates that gene-editing techniques may reduce harmful protein levels linked to these rare conditions. With dedicated scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel at the forefront, there is a shared personal motivation driving the quest for effective therapies. Although the road to human trials is lengthy and laden with challenges, the initial results show significant promise that one day, we may have viable treatments for prion diseases that can alter the course of these devastating disorders.