Suicide prevention for older adults is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention, especially as individuals aged 75 and above represent the age group with the highest suicide rates. Despite the alarming statistics, many senior citizens struggle to find mental health resources tailored to their unique needs. Research led by experts in geriatric psychiatry underscores the significant gap in online health information for seniors seeking assistance, highlighting the inadequacy of current suicide prevention efforts. As social isolation and loneliness contribute to this crisis, improving access to targeted resources becomes crucial. By raising awareness of elderly suicide prevention, we can foster an environment that prioritizes mental well-being among our aging population and offers them the support they rightfully deserve.
The topic of suicide prevention for the elderly highlights a critical need for specialized interventions aimed at our older community members. As we explore this vital area, it becomes clear that senior citizens frequently encounter barriers when accessing tailored mental health support. Notably, rising suicide rates in seniors illustrate the urgency for innovative solutions that address their unique challenges and circumstances. Alternative approaches to elderly suicide prevention can provide essential help, ensuring that comprehensive mental health resources are available and easily navigable for this vulnerable demographic. Fostering dialogue around geriatric mental health services is essential to combatting the rising tide of distress among older adults.
Understanding the High Suicide Rates in Seniors
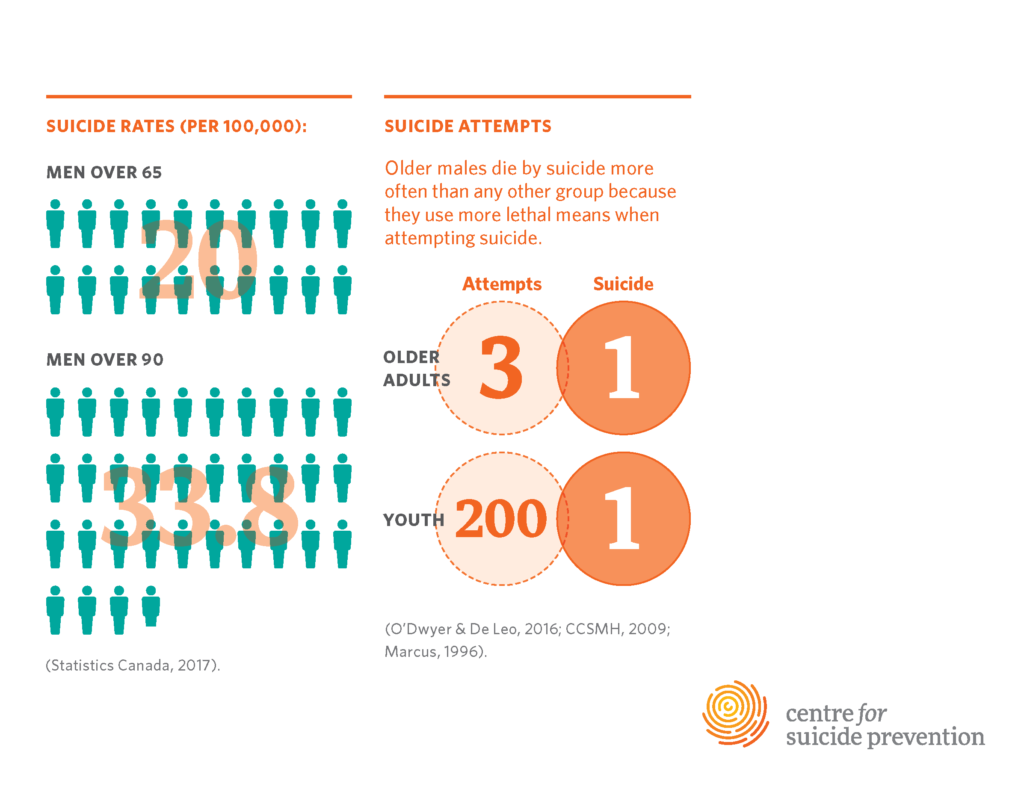
Suicide rates among older adults, particularly those aged 75 and above, are alarmingly high. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this demographic experiences one of the highest suicide rates, estimated at 20.3 per 100,000. This troubling statistic highlights a public health crisis that requires immediate attention, particularly as it contrasts sharply with declining suicide rates in younger age groups. Factors such as social isolation and chronic health issues exacerbate this situation, necessitating a deeper understanding of the mental health resources available specifically for seniors.
It is essential to recognize that many older adults suffer from loneliness and isolation, often due to loss of family, friends, or mobility challenges. This unfortunate reality can lead to increased feelings of despair and hopelessness, making them vulnerable to suicidal thoughts. Implementing effective suicide prevention strategies tailored to older adults is crucial. By increasing accessibility to mental health resources and encouraging supportive community connections, we can help combat these distressing trends.
The Need for Targeted Suicide Prevention Programs
Despite the visible need, there remains a significant gap in targeted suicide prevention efforts for older adults. Most existing programs and resources tend to focus on younger populations, often neglecting the distinct challenges faced by seniors. The findings from a recent study conducted by researchers at McLean Hospital highlight this disparity, revealing that even well-known national organizations fail to provide adequate resources specifically for older individuals. Addressing these gaps is vital, as tailored programs could significantly reduce the incidence of suicide among this vulnerable group.
To bridge this gap, there is a pressing need for targeted campaigns that consider the unique healthcare needs of older adults. This includes fostering an environment that encourages open discussions around mental health while simultaneously offering accessible online health information for seniors. By improving visibility and outreach of these resources, older adults may feel more empowered to seek help and support, ultimately reducing the stigma surrounding mental health issues in this age group.
Geriatric Psychiatry: A Critical Component in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a fundamental role in addressing the mental health challenges faced by older adults, particularly as it relates to suicide prevention. This specialized field of medicine is dedicated to understanding the psychiatric issues experienced by elderly individuals, ensuring that clinicians are well-equipped to provide effective and compassionate care. By integrating geriatric psychiatry principles into suicide prevention strategies, healthcare providers can offer solutions that address the root causes of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among seniors.
Moreover, geriatric psychiatrists emphasize the importance of assessing the overall mental health of older adults, which can often involve understanding the interplay between physical health and psychological well-being. This holistic approach not only aids in identifying those at risk but also fosters a comprehensive treatment framework that includes therapy, medication, and community-based support. The need for additional funding and research focused on geriatric psychiatry will be pivotal in reducing suicide rates in this demographic.
Empowering Seniors with Online Health Information
With the increasing utilization of the internet among older adults, there is a unique opportunity to empower seniors with online health information that can aid in suicide prevention. However, the findings from research indicate that existing resources are often not tailored to meet the specific questions and needs of this population. Creating user-friendly platforms that serve targeted information will be essential in ensuring that older adults can easily find and access relevant mental health resources.
Additionally, it is vital that seniors are guided on how to effectively navigate online health information for their needs. Programs aimed at digital literacy could assist older adults in understanding how to seek out credible resources and recognize red flags that necessitate professional help. By equipping them with the knowledge and tools to access mental health information, we can foster resilience and proactive management of their mental well-being.
Community Support and Social Connections
Building strong community connections is critical in preventing suicide among older adults. Social support networks can significantly lessen feelings of isolation and provide seniors with the companionship and encouragement they need to cope with life’s challenges. Local community initiatives, such as clubs, mentoring programs, and outreach services, can serve as vital components in promoting mental health and well-being for seniors. When individuals feel supported within their community, they are more likely to reach out for help when needed.
Additionally, community organizations can work on developing programs specifically aimed at older adults to foster an inclusive atmosphere that encourages dialogue about mental health issues. Initiatives that bring together seniors for activities—whether they are educational, recreational, or therapeutic—can strengthen their social ties and reduce the risk of suicide. A proactive approach in creating relationships can lead to a more substantial understanding of the importance of mental health and the resources available.
Clinical Interventions in Elderly Suicide Prevention
Clinical interventions are pivotal in addressing the mental health needs of older adults at risk for suicide. By employing evidence-based practices that are sensitive to the experiences and backgrounds of seniors, healthcare providers can make a significant impact in preventing suicide. Interventions may include cognitive-behavioral therapy tailored for older adults, medication management, and comprehensive assessments to monitor individuals’ mental health status regularly.
Healthcare systems should also prioritize training for clinicians in geriatric psychiatry, enabling them to recognize signs of distress among seniors effectively. Collaboration with geriatric specialists can enhance existing care models and ensure seniors receive the appropriate support. With a multidisciplinary approach, we can develop targeted treatment plans that effectively address the complex needs of older adults and ultimately mitigate suicide rates in this vulnerable population.
Importance of Research in Geriatric Mental Health
Research is essential in understanding the unique aspects of mental health in older adults and how it contributes to suicide prevention. Studies that focus on the prevalence of mood disorders, cognitive decline, and the effects of life transitions, such as retirement or losing a loved one, can provide vital insights into the mental health landscape of this community. This information can inform the development of targeted interventions and educational programs.
Additionally, garnering additional research funding dedicated to geriatric mental health can lead to breakthroughs in our understanding of elderly suicide prevention strategies. Collectively, researchers and practitioners can work to identify causal factors, improve access to mental health services, and inform policies that directly impact the health and well-being of older adults. Highlighting the importance of ongoing research will ultimately lead to a safer, healthier future for our aging population.
The Role of Family in Suicide Prevention
Family involvement is a crucial element in suicide prevention among older adults. Family members often serve as the first line of defense in recognizing changes in behavior, mood, or social interaction that could indicate a mental health crisis. Encouraging open conversations within families about mental health can help reduce the stigma associated with seeking help, fostering an environment where older adults feel safe discussing their feelings and struggles.
Educating families on how to identify warning signs and respond effectively can make a considerable difference in an older person’s life. When family members are informed about local mental health resources and how to approach their loved ones, they can offer support and encourage seniors to seek professional help. Establishing strong communication lines and familial support increases the likelihood that older adults will engage in healthier coping mechanisms, reducing the risk of suicide.
Advocating for Policy Change in Suicide Prevention
Advocacy for policy change is essential in enhancing suicide prevention efforts tailored to older adults. By influencing public health policies and funding for geriatric mental health programs, advocates can help ensure that resources are allocated appropriately. Policymakers must recognize the unique challenges faced by older adults and the pressing need for effective intervention strategies that address their specific needs.
Creating awareness around the issue of elderly suicide and influencing change within the healthcare system can lead to more comprehensive support for aging populations. Engaging stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, families, and community organizations, can ultimately strengthen campaigns aimed at reducing suicide rates among seniors. Collective action can spur positive shifts in how society views and addresses the mental health needs of older adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors influencing suicide rates in seniors?
Suicide rates in seniors, particularly those aged 75 and older, are influenced by several key factors, including social isolation, loneliness, and representational biases in research. These factors contribute to older adults feeling disconnected and underserved, making it imperative to improve mental health resources specifically tailored for elderly suicide prevention.
How can family members support elderly individuals at risk of suicide?
Family members can support elderly individuals at risk of suicide by fostering open communication about mental health and encouraging them to seek help from geriatric psychiatry professionals. It’s essential to be aware of warning signs and provide resources for suicide prevention specifically designed for older adults, ensuring they feel supported and understood.
What online health information is available to help prevent suicide in older adults?
Online health information for seniors concerning suicide prevention can be found on various reputable nonprofit organizations’ websites. However, a recent study found that resources specifically targeting older adults are often scarce and not easily accessible. It is crucial for organizations to develop targeted online materials that address the unique needs of this population.
Why are older adults at a higher risk for suicide?
Older adults are at a higher risk for suicide due to factors such as chronic illness, loss of loved ones, social isolation, and mental health issues like depression. The increased suicide rates among seniors highlight the urgent need for improved elderly suicide prevention strategies and targeted mental health resources.
What resources are essential for suicide prevention in older adults?
Essential resources for suicide prevention in older adults include accessible mental health services, community support programs, and online platforms that provide information on geriatric psychiatry. Tailored interventions focusing on the unique challenges faced by older adults are necessary to effectively reduce suicide rates in this demographic.
How can community programs assist in elderly suicide prevention?
Community programs can play a significant role in elderly suicide prevention by offering social engagement opportunities, mental health services, and educational workshops. These initiatives should focus on reducing social isolation among seniors and providing them with access to the necessary mental health resources for timely support.
What is the role of geriatric psychiatry in suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by assessing mental health issues, providing tailored treatments, and facilitating access to mental health resources. Specialists in this field are trained to understand the unique psychological and medical needs of older adults, making them vital to effective elderly suicide prevention efforts.
What steps can organizations take to improve suicide prevention resources for seniors?
Organizations can improve suicide prevention resources for seniors by creating easily navigable online platforms, conducting research to understand the specific needs of this population, and developing outreach campaigns that resonate with older adults. Increased funding for these initiatives is also essential for addressing the current imbalances in suicide prevention efforts.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults at Highest Risk | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest rates of suicide compared to other age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations lack accessible resources specifically targeting older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research found an imbalance in online resources, with few targeting older adults seeking help. |
| Suicide Rates | The CDC reports a rising suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000 in those over 75, while rates in younger groups decline. |
| Need for Targeted Campaigns | Proposed need for public-facing suicide prevention campaigns tailored for older adults. |
| Future Steps | Focus on funding, research, and creating easily accessible prevention programs for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is an emergent topic that demands urgent attention as this demographic constitutes the highest risk group for suicide. Despite the recognition of their vulnerability, there remains a significant lack of accessible resources tailored to their specific needs. Research shows that suicide rates among those aged 75 and over are rising, highlighting the importance of developing targeted campaigns and programming to address this issue. It is crucial for public health organizations to bridge the gap and provide comprehensive support for older adults seeking help with mental health challenges.