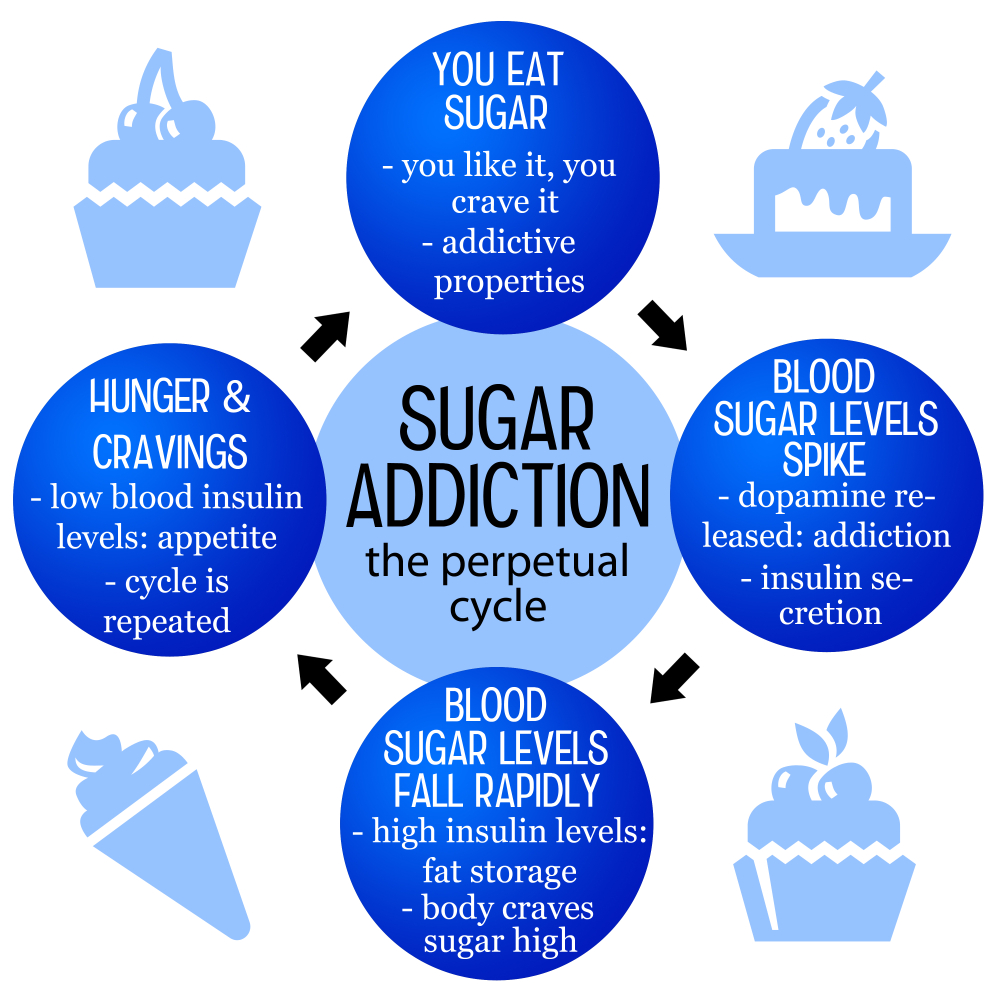
Is sugar addictive? This question often sparks lively debates among health experts, nutrition researchers, and everyday consumers alike. While sugar has been shown to induce cravings and even compulsive behaviors similar to some substances we typically classify as addictive, it does not meet the stringent criteria that categorize nicotine or alcohol as such. The effects of sugar consumption can lead to unhealthy eating patterns, particularly due to the prevalence of foods rich in added sugars within our modern diet. Understanding sugar addiction is crucial as harmful sugar intake not only affects our physical health but can also impact our mental well-being, illustrating the complex interplay between nutrition and sugar cravings in our lives.
Exploring the concept of sugar addiction involves looking at the enticing allure of this sweet substance, which many feel compelled to consume. Often likened to habits associated with more severe dependencies like tobacco or alcohol, the notion suggests that our bodies can develop an unhealthy relationship with sweets, leading to an uncontrollable desire for sugary snacks. This phenomenon raises important questions about dietary habits and their long-term effects on health, especially as we navigate the abundance of processed foods laden with excessive sugar. The psychological and physiological impact of excessive sugar consumption underscores the distinction between our need for nutrients and the compulsion that can arise from regularly indulging in sugary treats. Ultimately, whether framed as sugar addiction or simply as a deep-rooted craving, understanding this relationship is vital as we strive for healthier eating patterns.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a contentious issue among nutritionists and scientists. While substances like alcohol and nicotine provoke severe withdrawal symptoms and meet the criteria for addiction, sugar operates differently. Although sugar can provoke intense cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors similar to addictive substances, it is categorized more as a habit-forming food rather than a true addiction. Many people find themselves reaching for sugary snacks or drinks out of habit, driven by the brain’s reward system that responds to sugar intake with pleasure. This is compounded by the ubiquity of sugar-laden processed foods in our diets.
The harmful effects of sugar addiction can manifest in various ways, including increased body weight, heightened risk of metabolic disorders, and negative impacts on mental health. Frequent consumption of high-sugar foods can create a cycle of cravings and habitual eating, making it challenging to reduce intake. Nutrition experts like Frank Hu emphasize the importance of mindful consumption and moderation. They encourage individuals to be aware of the added sugars in their diet, as excessive intake can resemble other addiction patterns, leading people to experience withdrawal symptoms when trying to cut back.
The Effects of Sugar on the Body
The effects of sugar on the body go beyond mere weight gain; they can contribute to a host of health issues, including inflammation, diabetes, and heart disease. The body processes sugar quickly, leading to spikes in blood glucose levels, which can trigger a cycle of energy crashes and cravings. This cycle makes it difficult for individuals to maintain a balanced diet as they may constantly seek sugar for an energy boost. Additionally, excessive sugar intake can lead to fat accumulation in the liver, a condition that has become increasingly common and can lead to serious health complications if left unchecked.
Moreover, sugar influences neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly those involved in mood regulation. High sugar consumption is linked to mood swings and anxiety, contributing to an emotional reliance on sugary foods. Nutrition research suggests that moderating sugar intake can help stabilize mood and energy levels over time, leading to better overall health. To mitigate these effects, individuals should focus on a well-rounded diet rich in whole foods that provide balanced nutrition without relying on added sugars.
Coping with Sugar Cravings
Coping with sugar cravings can be a challenge, especially for those accustomed to a diet high in sugary snacks and beverages. Recognizing these cravings is the first step towards managing them effectively. Nutritionists suggest implementing strategies such as increasing fiber intake and consuming protein-rich foods which can help maintain blood sugar levels and curb cravings. Substituting processed snacks with healthier options, such as fruits and nuts, can also alleviate the pull towards sugary foods while still satisfying the need for a treat.
Behavioral strategies can also be effective in addressing sugar cravings. Mindful eating practices encourage individuals to slow down and savor their food, which can lead to greater satisfaction and a reduced desire for excessive sweetness. Additionally, understanding the triggers for these cravings—such as stress or boredom—can provide insight into when and why they occur. By developing a more conscious relationship with food, individuals can enjoy the sweetness of sugar without falling into the trap of dependency.
Nutrition and Sugar: Finding a Balance
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in understanding how sugar fits into a healthy lifestyle. While sugar is often demonized, it is important to distinguish between naturally occurring sugars in fruits and dairy and added sugars found in processed foods. The World Health Organization and other health organizations recommend limiting added sugars to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Recognizing this distinction can empower individuals to make healthier choices while still enjoying sweets occasionally within the context of a balanced diet.
Establishing guidelines for sugar intake based on nutrition can also promote awareness and proactive choices. The American Heart Association sets specific limits on daily added sugar consumption, urging individuals to become adept at reading food labels and understanding ingredient lists. By educating oneself about sugar content in foods, individuals can better navigate their dietary preferences and prioritize nutrient-dense foods that nourish the body rather than lead to cravings and potential addiction.
Harmful Effects of Excess Sugar Intake
Excess sugar intake has been linked to a range of negative health outcomes, including obesity, insulin resistance, and heart disease. Studies indicate that high consumption of added sugars can lead to increased visceral fat accumulation, which is particularly harmful as it surrounds vital organs. This type of fat is associated with a higher risk of developing chronic conditions, highlighting the direct relationship between sugar consumption and health complications.
Beyond physical health, the harmful effects of sugar can extend to mental well-being. Emerging research suggests that high sugar diets may be correlated with increased levels of anxiety and depression. This connection emphasizes the need for careful monitoring of sugar intake as part of a holistic approach to health. Limiting added sugars while maintaining a nutrient-rich diet can positively impact both physical health and emotional stability.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar in Your Diet
Reducing sugar in your diet doesn’t have to be a daunting task. Start by gradually decreasing your sugar intake rather than going cold turkey, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms and increased cravings. For instance, you might cut back by replacing sugary breakfast cereals with oatmeal or smoothies and opting for unsweetened beverages instead of soda. Gradual changes help your taste buds adjust and make the transition smoother, ultimately leading to a preference for less sweet flavors.
Another effective strategy is to incorporate more whole foods into your meals. Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits provide essential nutrients that can keep you satiated without the need for added sugars. Experimenting with spices such as cinnamon or vanilla can add a natural sweetness to dishes, reducing the need for processed sugar. By mastering these strategies, individuals can enjoy a more balanced diet while mitigating the cravings that often accompany high sugar intake.
The Role of Sugar in Our Lives
Sugar plays a multifaceted role in our lives—it’s not only a source of energy but also a key ingredient that contributes to the enjoyment of food. Sweetness can enhance flavor and create positive associations with certain foods and experiences, from celebratory cakes to holiday treats. Acknowledging the positive aspects of sugar can help establish a more balanced approach to consuming it, allowing individuals to appreciate it without obsession or excessive guilt.
At the same time, it’s crucial to remain mindful of how much sugar is consumed within the context of overall health. While sugar can brighten meals and elevate mood, it’s essential to make informed choices about its intake. By adopting a culture of moderation rather than restriction, we can enjoy the pleasures that sugar brings while safeguarding our health and well-being.
Mindful Eating: A Solution for Sugar Cravings
Mindful eating is an effective strategy for combating sugar cravings and fostering a positive relationship with food. This practice involves paying attention to the sensory experience of eating—tasting, smelling, and appreciating each bite. By slowing down and being present during meals, individuals are more likely to recognize their body’s hunger cues and satiety signals. This can prevent overeating and help to curb the desire for sugar-laden foods.
Incorporating mindful eating into daily habits also helps individuals become more aware of their emotional triggers for consuming sugar. Many people turn to sweets for comfort, which can create a cycle of emotional eating. By learning to recognize these patterns, individuals can seek healthier coping mechanisms and address the underlying emotions driving their cravings. Mindful practices can transform the approach to eating, turning it into a nourishing experience rather than one driven by habit or impulse.
Conclusion: Is Sugar Addictive?
In conclusion, the question of whether sugar is addictive remains complex and nuanced. While it does not meet the strict clinical definitions of addiction found in substances like alcohol and nicotine, the psychological and physiological effects of sugar can mimic addictive behaviors. Understanding these nuances allows for a more balanced perspective, enabling individuals to enjoy sugar in moderation without succumbing to extreme cravings or unhealthy eating habits.
Ultimately, managing sugar intake is about finding the right balance. With informed choices and mindful consumption, individuals can appreciate the sweetness of sugar without it interfering with their overall health and well-being. The goal is to incorporate sugar sensibly into a well-rounded diet that prioritizes nutrition and health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive and how does it affect our cravings?
Sugar can produce effects similar to addictive substances by increasing cravings and encouraging compulsive eating behaviors. However, it doesn’t meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like alcohol or nicotine. The addictive qualities of sugar are influenced by its presence in highly processed foods that heighten cravings.
What are the harmful effects of sugar addiction on our health?
While sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance, excessive intake can lead to health issues. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which can contribute to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Monitoring sugar intake is crucial to prevent these harmful effects.
Is sugar craving a sign of sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings can be a sign of dependency on sugary foods but do not definitively indicate sugar addiction as classified with substances like alcohol. The addictive nature of sugar lies in the body’s response to highly palatable processed foods that contain sugar.
How does nutrition and sugar intake impact our overall health?
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in how sugar affects our health. While some sugar is necessary for energy, high amounts of added sugar, particularly from processed foods, can lead to negative health outcomes. Balancing sugar intake within recommended limits is vital for health.
What should I know about my sugar intake to avoid sugar addiction?
To avoid potential sugar addiction, it’s important to be aware of your added sugar intake. The American Heart Association suggests limits on daily sugar consumption: 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women. Gradually reducing sugar intake and reading food labels can help manage cravings effectively.
Can we eliminate sugar entirely from our diets?
While it’s possible to eliminate added sugars, complete removal of sugar from your diet isn’t feasible as it naturally occurs in many foods like fruits and milk. The key is to consume sugar in moderation and focus on whole foods while avoiding highly processed sugar-laden products.
Are there withdrawal symptoms associated with sugar addiction?
When reducing sugar intake, some individuals report mild withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and dizziness. While these symptoms are less severe than those from substances like alcohol, they indicate a psychological dependency on sugar-rich foods.
What role does sugar play in our diets?
Sugar enhances the flavor and texture of food and is a part of a balanced diet when consumed in appropriate amounts. It is essential to differentiate between necessary dietary sugars found in whole foods and harmful added sugars in processed items.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition of Sugar Addiction | Sugar is debated as addictive, similar to alcohol and nicotine, but does not meet strict clinical criteria for addiction. |
| Effects of Sugar Consumption | Increased cravings and compulsive behaviors can result from sugar, leading to withdrawal-like symptoms when eliminated. |
| Processed Foods | Ultraprocessed foods with added sugar can heighten cravings, making them hard to resist. |
| Importance of Moderation | Low to moderate sugar intake is generally safe, with dosage important for health effects. |
| Recommendations | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked much debate among health experts. While sugar does have some addictive qualities due to its impact on cravings and consumption patterns, it is not classified in the same category as substances like alcohol or nicotine. Moderation and awareness of sugar intake are key to maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle.