Bile imbalance and liver cancer are increasingly recognized as integral factors in the realm of liver diseases, particularly in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Recent studies have highlighted how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to harmful liver conditions, underscoring the potential connection between these imbalances and the progression of cancer. Key findings reveal that the gut’s bile production, which plays a vital role in fat digestion and metabolic regulation, can significantly impact liver health. The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) serves as a crucial molecular switch that, when inhibited, leads to excessive bile acid accumulation, inflammation, and even tumor formation. Understanding these mechanisms not only paves the way for innovative cancer treatments but also reinforces the importance of maintaining proper bile acid homeostasis to combat liver diseases.
The relationship between bile dysregulation and hepatic malignancies, such as liver carcinoma, reveals a complex interplay that demands attention. Imbalances in bile acids—necessary compounds for efficient fat digestion—can induce serious liver-related issues, especially when coupled with the negative implications of compromised FXR function. Emerging research shows that the lack of proper bile acid metabolism can precipitate conditions conducive to liver cancer, particularly through pathways that govern cell growth and response to metabolic cues. In this light, targeted cancer therapies focusing on revitalizing biliary health could be essential in mitigating risks associated with liver diseases. This broader understanding underscores the significance of maintaining optimal bile levels for overall liver integrity and cancer prevention.
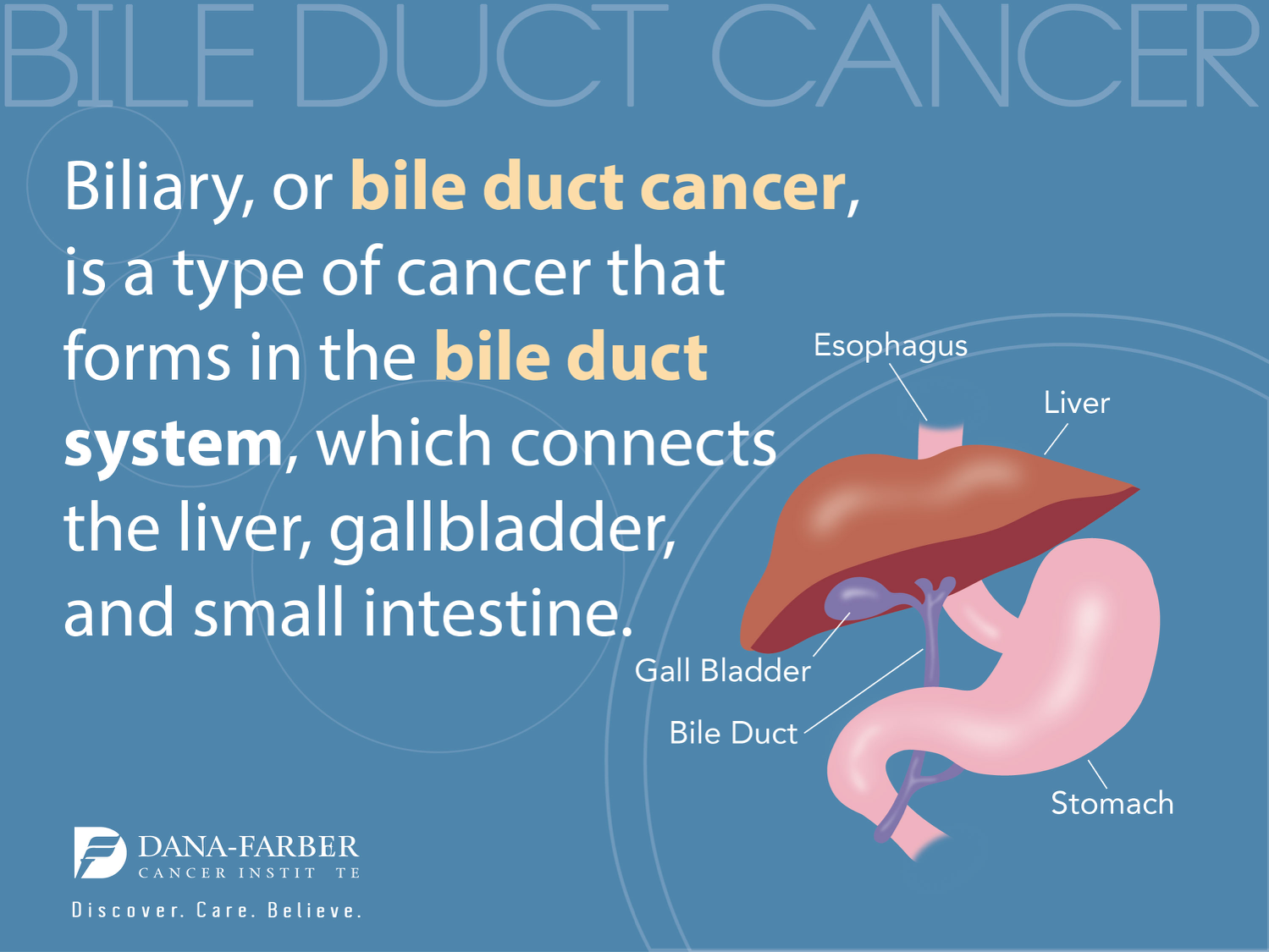
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Connection to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance occurs when the liver fails to produce the correct composition of bile acids necessary for proper digestion and metabolism. This condition is critical because bile acids not only assist in fat digestion but also play a significant role in signaling pathways within the liver. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to inflammation, liver fibrosis, and ultimately increase the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. A comprehensive understanding of bile acid homeostasis is essential in investigating liver diseases, as the liver’s ability to maintain this balance is vital for overall health.
Recent research indicates that a previously undocumented molecular switch involving the protein YAP significantly affects bile acid metabolism. By repressing the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), YAP exacerbates bile acid overproduction. This accumulation not only triggers liver injury but also creates an environment conducive to malignant transformations, leading to liver cancer. Recognizing this connection underlines the need for effective approaches in managing bile imbalances to potentially prevent liver cancer progression.
The Role of FXR in Bile Acid Metabolism and Cancer Prevention
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is critical in regulating bile acid synthesis and transport, acting as a master regulator for bile homeostasis. When FXR function is compromised, as seen in conditions where YAP is activated, bile acids can accumulate to toxic levels, causing cellular damage and promoting liver diseases, including HCC. Enhancing FXR’s activity could present a potent avenue in cancer prevention and treatment, as restoring its function may help rebalance bile acids and reduce inflammation in the liver.
Recent studies have shown promising results in therapies aimed at activating FXR, which may halt the progression towards liver cancer by ameliorating the detrimental effects of bile acid overload. Such pharmacological interventions could be pivotal in not only treating liver disease but also preventing hepatocellular carcinoma in at-risk populations. The ongoing research in this area underscores the potential of targeting FXR in cancer treatment paradigms by harnessing the liver’s natural detoxification processes.
Cell Signaling Pathways Involving Hippo/YAP and Liver Diseases
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth and metabolic functions in the liver. When YAP is overexpressed, it may lead to increased cell proliferation and tumor formation by disrupting normal liver function, particularly in bile acid metabolism. This dysregulation may result in inflammatory responses and contribute to the progression of liver diseases, highlighting how vital proper signaling is for maintaining liver health. Investigating how cell signaling pathways interact with metabolic processes can unveil new therapeutic targets.
Understanding the impacts of the Hippo/YAP pathway on liver diseases aids researchers in developing targeted treatments for conditions like HCC. By elucidating the mechanisms of how YAP modulates bile acid metabolism and liver inflammation, potential strategies can be devised to counteract these effects. Therapies that can either inhibit YAP activity or boost FXR function are of particular interest, as they could mitigate liver damage while concurrently reducing the risk of cancer development.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
As research into liver cancer continues to evolve, understanding the underlying mechanisms of bile acid metabolism is becoming increasingly critical. Current studies highlight the importance of molecular regulators like YAP and FXR in the pathogenesis of liver diseases, suggesting that therapies designed to enhance FXR function may represent a significant breakthrough. Novel approaches could involve the use of FXR agonists or other compounds that restore bile acid homeostasis, therefore potentially lowering the incidence of liver cancer.
The exploration of therapeutic avenues that address bile imbalance and its consequent effects on liver health will be crucial in future liver cancer research. As scientists better understand the intricate connections between bile acids, liver inflammation, and cancer development, there is great potential for emerging treatment protocols that can significantly alter treatment outcomes for patients facing the threat of liver disease and HCC.
Impact of Bile Acid Accumulation on Liver Health
Bile acid accumulation in the liver can promote a cascade of detrimental effects that lead to significant liver damage. This toxicity can initiate a complex interplay of inflammatory responses that foster conditions suitable for the progression of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. As bile acids are also involved in metabolic signaling, their dysregulation underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy bile acid pool to support liver health and prevent disease.
The recognition that excess bile acids may contribute to liver pathologies emphasizes the need for strategies to promote bile acid clearance from the liver. Research into medication that can enhance the excretion of bile acids might provide a therapeutic angle to not only improve liver function but also reduce the risk of developing liver cancer. These insights reinforce the critical relationship between bile composition, metabolic health, and cancer risks.
Pharmacological Approaches in Treating Liver Diseases
Recent advancements in pharmacological treatments targeting liver diseases are focusing on the nuanced regulation of bile acid metabolism through FXR activation. Drugs that stimulate FXR’s function have shown promise in preclinical studies, suggesting they could mitigate the toxic effects of bile acid overload in the liver. Such therapies are not only crucial for addressing established liver diseases but also for preventing the progression to more severe conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, research into combinations of treatments—such as simultaneously activating FXR while inhibiting pathways like YAP—could yield synergistic effects, further refining therapeutic strategies for liver conditions. As the understanding of bile acid dynamics continues to grow, innovative pharmacological interventions may emerge, paving the way for more effective liver cancer treatments and enhanced patient outcomes.
Lifestyle Interventions for Liver Health
In addition to pharmacological strategies, lifestyle interventions play a significant role in maintaining liver health and preventing bile imbalance. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and adequate fiber can support healthy bile acid metabolism and overall liver function. Regular exercise has also been shown to positively impact liver health by improving metabolic processes and reducing the risk of liver diseases, including cancer.
Adopting healthier lifestyle choices not only aids in the regulation of bile acids but also enhances the body’s ability to manage inflammation and stressors that contribute to liver damage. Education on the importance of liver health and proactive measures to maintain bile balance will be critical in reducing the incidence of liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma in the general population.
Ongoing Research and Developments in Liver Cancer Treatments
Ongoing research in the field of liver cancer treatment is increasingly focusing on the intersections between metabolic health, bile acid modulation, and cancer progression. Cutting-edge studies are exploring new therapeutic agents that can manipulate bile acid signaling and restore homeostasis in the liver. The identification of molecular targets, such as YAP and FXR, has opened up innovative avenues for developing effective treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma.
As the scientific community continues to delve deeper into the molecular mechanisms that underlie liver diseases, the potential for groundbreaking therapies expands. Encouraging results from clinical trials aimed at improving bile acid metabolism and liver function offer hope for the future of liver cancer treatment, making it an exciting time for researchers and patients alike.
Educational Outreach and Awareness on Liver Health
Raising awareness about liver health and the impacts of bile imbalance is essential for the prevention and early detection of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Public health campaigns focusing on the importance of liver function and promoting routine medical check-ups can empower individuals to take charge of their liver health. Providing information about the signs of liver dysfunction and the role of bile acids can help mitigate risks associated with liver cancer.
Educational programs should also emphasize the significance of healthy lifestyle choices and the management of risk factors that contribute to liver disease. By informing individuals about the critical connections between bile acid metabolism, liver function, and cancer risk, health initiatives can foster a more proactive approach to liver health, potentially reducing liver disease prevalence and improving community well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does bile imbalance contribute to liver cancer development?
Bile imbalance can lead to liver injury and inflammation, ultimately triggering the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This occurs when disruptions in bile acid metabolism result in the overproduction of bile acids, leading to fibrosis in the liver, which is a precursor to cancer.
What role does FXR function play in bile acid metabolism related to liver cancer?
FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) is essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When FXR function is inhibited, it can result in bile acid overproduction and accumulation in the liver, increasing the risk of liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Enhancing FXR activity is a potential strategy for cancer prevention and treatment.
What is the link between bile acid metabolism and hepatocellular carcinoma?
Bile acid metabolism is closely linked to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as imbalances in bile acids can promote liver injury and inflammation, leading to cancer. The study shows that the regulation of bile acids through pathways involving FXR and YAP is critical in preventing HCC.
Can enhancing FXR function help prevent liver cancer?
Yes, enhancing FXR function can help restore bile acid balance and prevent liver damage, thereby reducing the risk of liver cancer. Research indicates that activating FXR could stop the harmful cycle of bile acid overproduction associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.
What impact does the inhibition of YAP have on bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
YAP inhibition may positively affect bile acid metabolism by allowing FXR to function appropriately, thus preventing bile acid accumulation. This can potentially reduce inflammation and fibrosis in the liver, lowering the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What are the potential treatment strategies for liver cancer related to bile imbalance?
Potential treatment strategies include pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR, inhibit YAP’s repressor function, or increase bile acid excretion. These strategies aim to restore bile acid homeostasis and prevent the progression of liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma.
How does liver inflammation relate to bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
Liver inflammation can result from bile acid imbalance, which causes cellular damage and fibrosis. Chronic inflammation in the liver is a significant risk factor for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as the inflammatory environment encourages cancerous changes in the liver cells.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Findings | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The study identifies a molecular switch that may lead to new treatments. |
| Role of Bile Acids | Bile acids help digest fats and also regulate metabolic processes, acting like hormones. |
| Key Researcher | Yingzi Yang, a professor at HSDM, studied how bile acid production regulation is linked to liver injury and cancer. |
| YAP Role | YAP (Yes-associated protein) inhibits FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), leading to bile acid overproduction, fibrosis, and inflammation. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s repressive function may enhance FXR function, promoting bile acid excretion and halting liver cancer progression. |
| Research Implications | YAP’s influence on nutrient sensing is vital, with potential links to broader metabolic processes and cancer. |
| Future Directions | Pharmacological solutions targeting FXR stimulation could be promising for liver cancer treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are critically linked, as recent research highlights the role of bile acids in liver disease progression. A study led by Yingzi Yang reveals that disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By identifying the molecular switch, YAP, which inhibits crucial bile acid metabolism pathways, the research opens new avenues for potential treatment interventions. Researchers suggest that targeting YAP and enhancing bile acid homeostasis may effectively prevent liver cancer development. Continued exploration in this area could lead to significant advancements in pharmacological treatments for liver-related diseases.